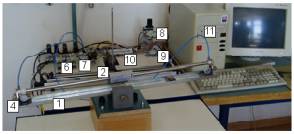
- Frame
- Rodless cylinder
- Rotational potentiometer for q
- Rotational potentiometer for x
- Electronic reference card
- Pressure transducer
- Proportional valve
- Pressure valve & filter
- Air supply valve
- Electronic interface
- Control computer
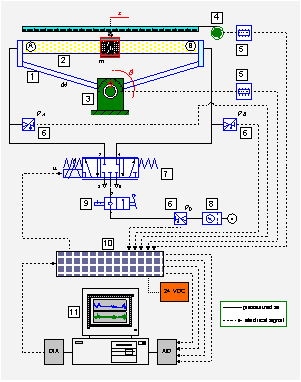
Research → Mechatronic systems → Pneumatically actuated inverted wedgeThe balancing mechanism of an inverted wedge system has fairly similar characteristics as an inverted pendulum system. In this control task, the objective is to design a controller for achieving a motion of the cylinder slider such that the frame of the wedge has horizontal position during the time. The controlled system should have zero steady state error in angle of the frame and satisfactory disturbance rejection properties. Movement of the slider is realized by pneumatics. Energy of compressed air can steer the slider of the cylinder left and right in order to keep the wedge in balance. The control system has one control input, which is the force proportional to the pressure difference between two cylinder chambers. There are two measured outputs of the system, which are the frame angle q and the slider position x. In a broader sense, this balancing mechanism can be considered as a two degrees- of-freedom planar robot controlled by a single control input. Because it is an under-actuated system with a non-minimum phase characteristic and nonlinear actuator dynamics, this experimental model offers great possibilities to learn design in a mechatronic way. Below figures illustrate the photo of the experimental setup (see experimental system description) and the schematic diagram of the pneumatically actuated inverted wedge. |
|
|
|
| Photography of inverted wedge | Schematic diagram of control system |
|
|
|
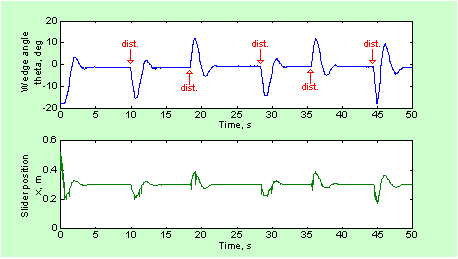
| Experimental results of inverted wedge balancing using state feedback controller |